PAT考试链表相关笔记
前置知识
数据定义
1 | struct Node { |
创建链表
1 | Node* create(vector<int> &arr) { |
查找元素
从第一个结点开始不断判断当前结点的数据域是否等于待查找元素
1 | int search(Node *head, int x) { |
插入元素
将x插入以head为头结点的链表的第pos个位置上,即插入完数据域为x的结点是第pos个结点(头结点后的第一个结点是一号位)
1 | void insert(Node *head, int pos, int x) { |
删除元素
删除链表上所有值为x的结点
1 | void del(Node *head, int x) { |
静态链表
对于五位数的地址,没有必要建立动态链表,使用静态链表会方便很多。
1 | struct Node { |
[1032] Sharing
题目
To store English words, one method is to use linked lists and store a word letter by letter. To save some space, we may let the words share the same sublist if they share the same suffix. For example, loading and being are stored as showed in Figure 1.
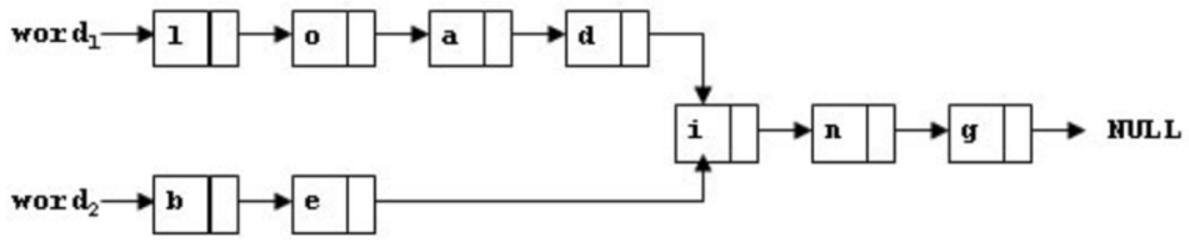
You are supposed to find the starting position of the common suffix (e.g. the position of i in Figure 1).
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains two addresses of nodes and a positive $N (<= 105)$, where the two addresses are the addresses of the first nodes of the two words, and $N$ is the total number of nodes. The address of a node is a 5-digit positive integer, and NULL is represented by $-1$.
Then $N$ lines follow, each describes a node in the format:
1 | Address Data Next |
where Address is the position of the node, Data is the letter contained by this node which is an English letter chosen from {a-z, A-Z}, and Next is the position of the next node.
Output Specification:
For each case, simply output the 5-digit starting position of the common suffix. If the two words have no common suffix, output -1 instead.
注意点与解析
- 求两个链表的⾸个共同结点的地址,如果没有,就输出-1.
- 测试点5:有可能数据相同但是地址不相同
- ⽤结构体数组存储,
node[i]表示地址为i的结点,key表示值,next为下⼀个结点的地址,flag表示第⼀条链表有没有该结点.遍历第⼀条链表,将访问过的结点的flag都标记为true,当遍历第⼆条结点的时候,如果遇到了true的结点就输出并结束程序,没有遇到就输出-1
代码
1 | struct Node { |
[1025] Reversing Linked List
题目
Given a constant $K$ and a singly linked list $L$, you are supposed to reverse the links of every $K$ elements on $L$. For example, given $L$ being 1→2→3→4→5→6, if $K=3$, then you must output 3→2→1→6→5→4; if $K=4$, you must output 4→3→2→1→5→6.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains the address of the first node, a positive $N (≤10^5)$ which is the total number of nodes, and a positive $K (≤N)$ which is the length of the sublist to be reversed. The address of a node is a 5-digit nonnegative integer, and NULL is represented by -1.
Then $N$ lines follow, each describes a node in the format:
1 | Address Data Next |
where Address is the position of the node, Data is an integer, and Next is the position of the next node.
Output Specification:
For each case, output the resulting ordered linked list. Each node occupies a line, and is printed in the same format as in the input.
注意点与解析
- 把地址为temp的数的数值存⼊data[temp]中,把temp的下⼀个结点的地址存⼊next[temp]中。
- 不⼀定所有的输⼊的结点都是有⽤的,加个计数器sum,并用list数组来存真正有用的数据,result存翻转的结果
代码
1 | int data[100005], next[100005], list[100005], result[100005]; |
[1052] Linked List Sorting
题目
A linked list consists of a series of structures, which are not necessarily adjacent in memory. We assume that each structure contains an integer key and a Next pointer to the next structure. Now given a linked list, you are supposed to sort the structures according to their key values in increasing order.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive $N (<10^5)$ and an address of the head node, where N is the total number of nodes in memory and the address of a node is a 5-digit positive integer. NULL is represented by $−1$.
Then $N$ lines follow, each describes a node in the format:
1 | Address Key Next |
where Address is the address of the node in memory, Key is an integer in $[−10^5, 10^5]$, and Next is the address of the next node. It is guaranteed that all the keys are distinct and there is no cycle in the linked list starting from the head node.
Output Specification:
For each test case, the output format is the same as that of the input, where $N$ is the total number of nodes in the list and all the nodes must be sorted order.
注意点与解析
- 定义静态链表。其中结点性质由
bool型变量flag定义,用以表示为结点在链表中是否出现。若当flag为false,则表示无效结点(不在链表上的结点)。 - 进行初始化。令
flag均为false表示初始状下所有结点都是无效结点 - 由题目给出的链表首地址遍历整条链表并标记有效结点的
flag为true,同时计数有效结点的个数count。 - 对结点进行排序。排序函数
cmp的排序原则是:如果cmp的两个参数结点中有无效结点,则按flag从大到小排序,以把有效结点排到数组左端(因为有效结点的flag为1大于无效结点的flag);否则,按数据域从小到大排序。 - 由于有效结点已经按照数据域从小到大排序,因此按要求输出有效结点即可。
- 注意:
- 可以直接使用
%05d的输出格式,以在不足5位时在高位补0。但是要注意-1不能使用%05d输出,否则会输出-0001(而不是-1或者-00001),因此必须要留意-1的输出。 - 题目可能会有无效结点,即不在题目给出的首地址开始的链表上。
- 数据里面还有全部是无效的情况,这时就要根据有效结点的个数特判输出
0 -1。
- 可以直接使用
代码
1 | int maxn = 100005; |
[1097] Deduplication on a Linked List
题目
Given a singly linked list $L$ with integer keys, you are supposed to remove the nodes with duplicated absolute values of the keys. That is, for each value $K$, only the first node of which the value or absolute value of its key equals $K$ will be kept. At the mean time, all the removed nodes must be kept in a separate list. For example, given $L$ being 21→-15→-15→-7→15, you must output 21→-15→-7, and the removed list -15→15.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains the address of the first node, and a positive $N (≤10^5)$ which is the total number of nodes. The address of a node is a 5-digit nonnegative integer, and NULL is represented by −1.
Then N lines follow, each describes a node in the format:
1 | Address Key Next |
where Address is the position of the node, Key is an integer of which absolute value is no more than $10^4$, and Next is the position of the next node.
Output Specification:
For each case, output the resulting linked list first, then the removed list. Each node occupies a line, and is printed in the same format as in the input.
注意点与解析
- 定义静态链表。其中结点性质由
int型变量order定义,用以表示结点在链表上的序号。由于最后需要先输出所有未删除的结点,然后输出所有被删除的结点,因此不妨在后面的步骤中令未删除的结点的order从0开始编号,被删除的结点的order从maxn开始编号 - 初始化。令
order的初值均为2maxn,这样无效结点就会被区分开来。 - 设置变量
countValid(初始化为0),用来记录未删除的有效结点的个数;设置countRemoved(初始化为0),用来记录被删除的有效结点的个数。由题目给出的链表首地址遍历整条链表,如果当前访问结点的权值的绝对值还未出现过(可以开一个全局的bool数组isExist来记录),那么就把该结点的order设为countValid,然后令countValid加1;如果当前访问结点的权值的绝对值已经出现过,那么就把结点的order设为maxn+countRemoved然后令countRemoved加1。这样未删除的结点的order就从0开始编号,而被删除的结点就从maxn开始编号。 - 对结点进行排序,排序函数
cmp的排序原则是:直接按照结点的order从小到大排序。由于未删除的结点的order从0开始编号,被删除的结点从maxn开始编号,而无效结点的order为初始的2maxn,因此结点的顺序就是按未删除的结点、已删除的结点、无效结点进行排列。 - 输出链表。记
count为countValid与countRemoved之和,之后将node[0]~node[count-1]输出。 - 注意:
- 最后一个未删除结点和最后一个被删除结点单独处理
- 题目可能会给出无效结点
代码
1 | int maxn = 100005; |