Hooks相关笔记和React项目创建步骤
Hooks部分参考自文档:https://beta.reactjs.org/apis/react
Hooks
memo
原型
memo的对象是组件component,一般是在父组件中为需要用的子组件套上,减少子组件渲染次数。即当父组件有多个子组件时,使用 memo,可以让没有 props 变化的子组件不渲染
1 | const MemoizedComponent = memo(SomeComponent, arePropsEqual?) |
使用
当重新渲染某个组件的时候,
React也会渲染它全部的子组件,这就会导致渲染的过程很慢。因此当组件的参数props和上一次是一样的时候其实就可以让它跳过,避免重复工作。
只有当name改变时才会重新渲染Greeting。1
2
3const Greeting = memo(function Greeting({ name }) {
return <h1>Hello, {name}!</h1>;
});当某个组件本身的
state被改变时,即使他被memo了它也会改变。
比如这个例子,输入名字来打招呼。当name名字属性不改变时不会重新渲染Greeting组件来打招呼(因为它被momo了)但是在它的内部通过useState来改变greeting的值,即打招呼的方式。每次setChange都改变了state,所以即使名字没有变,也会用新的方式来打招呼。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51export default function MyApp() {
const [name, setName] = useState('');
const [address, setAddress] = useState('');
return (
<>
<label>
Name{': '}
<input value={name} onChange={e => setName(e.target.value)} />
</label>
<label>
Address{': '}
<input value={address} onChange={e => setAddress(e.target.value)} />
</label>
<Greeting name={name} />
</>
);
}
const Greeting = memo(function Greeting({ name }) {
console.log('Greeting was rendered at', new Date().toLocaleTimeString());
const [greeting, setGreeting] = useState('Hello');
return (
<>
<h3>{greeting}{name && ', '}{name}!</h3>
<GreetingSelector value={greeting} onChange={setGreeting} />
</>
);
});
function GreetingSelector({ value, onChange }) {
return (
<>
<label>
<input
type="radio"
checked={value === 'Hello'}
onChange={e => onChange('Hello')}
/>
Regular greeting
</label>
<label>
<input
type="radio"
checked={value === 'Hello and welcome'}
onChange={e => onChange('Hello and welcome')}
/>
Enthusiastic greeting
</label>
</>
);
}在有些情况下即使使用了
memo,哪怕参数没变,组件也有可能会被重新渲染- 当这个被记忆的组件的参数并不是来自于它的父组件时
- 传入的参数是对象、数组、函数(所以对于参数是这些的组件
memo失效),因此最直接的方法就是可以将该对象or数组里的元素解耦出来,作单个参数一个个传入。
useCallback
原型
1 | const cachedFn = useCallback(fn, dependencies) |
- 第一个参数类型为
function,一个回调函数; - 第二个参数为一个列表,这个列表里的元素被称为依赖项,只有当这些依赖项更新时,这个回调函数才会执行并起作用,然后由
useCallback返回。
- 在每次重新渲染时,React会将第二个列表参数里的依赖项(元素)和上一次渲染的进行比较;如果都没有发生更改,
useCallback就不执行第一个回调函数;反之则执行。 - 缓存的对象是父组件传给子组件的函数,相当于对函数做了缓存,当父组件重新渲染时,函数不会重新定义,不会返回一个新的函数(注意是返回这个函数,并没有调用它)从而不会重新渲染。
useCallback要和React.memo配套使用,缺了一个都可能导致性能不升反而下降。
使用
当只是改变颜色主题时,跳过渲染。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88import { memo, useState, useCallback } from 'react';
export default function App() {
const [isDark, setIsDark] = useState(false);
return (
<>
<label>
<input
type="checkbox"
checked={isDark}
onChange={e => setIsDark(e.target.checked)}
/>
Dark mode
</label>
<hr />
<ProductPage
referrerId="wizard_of_oz"
productId={123}
theme={isDark ? 'dark' : 'light'}
/>
</>
);
}
function ProductPage({ productId, referrer, theme }) {
const handleSubmit = useCallback((orderDetails) => {
post('/product/' + productId + '/buy', {
referrer,
orderDetails,
});
}, [productId, referrer]);
return (
<div className={theme}>
<ShippingForm onSubmit={handleSubmit} />
</div>
);
}
function post(url, data) {
// Imagine this sends a request...
console.log('POST /' + url);
console.log(data);
}
const ShippingForm = memo(function ShippingForm({ onSubmit }) {
const [count, setCount] = useState(1);
console.log('[ARTIFICIALLY SLOW] Rendering <ShippingForm />');
let startTime = performance.now();
while (performance.now() - startTime < 500) {
// Do nothing for 500 ms to emulate extremely slow code
}
function handleSubmit(e) {
e.preventDefault();
const formData = new FormData(e.target);
const orderDetails = {
...Object.fromEntries(formData),
count
};
onSubmit(orderDetails);
}
return (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<p><b>Note: <code>ShippingForm</code> is artificially slowed down!</b></p>
<label>
Number of items:
<button type="button" onClick={() => setCount(count - 1)}>–</button>
{count}
<button type="button" onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>+</button>
</label>
<label>
Street:
<input name="street" />
</label>
<label>
City:
<input name="city" />
</label>
<label>
Postal code:
<input name="zipCode" />
</label>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
);
});根据上一次回调中的状态更新下一次新的状态。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7function TodoList() {
const [todos, setTodos] = useState([]);
const handleAddTodo = useCallback((text) => {
const newTodo = { id: nextId++, text };
setTodos(todos => [...todos, newTodo]);
}, []);
}
useMemo
原型
1 | const cachedValue = useMemo(calculateValue, dependencies) |
和 useCallback 很像,都是在依赖数据发生变化的时候,才会调用传进去的回调函数去重新计算结果,起到一个缓存的作用。
useCallback缓存的结果是函数,主要用于缓存函数(没有调用这个函数)一般会是函数组件。- 但
useMemo缓存的结果是回调函数中return回来的值——计算结果的值;即函数被调用,得到这个函数调用后返回的值,然后再返回这个值。 - 有两个参数:
- 第一个是没有参数的回调函数,比如
() =>,通过这个回调函数返回你想要缓存的值; - 依赖项列表,里面包含着在第一个函数参数里计算要用的变量。
- 第一个是没有参数的回调函数,比如
使用
1 | import { useState, useMemo } from 'react'; |
useContext
原型
1 | const value = useContext(SomeContext) |
使用
- 在各层组件之间上下搜索
ThemeContext的值,找到最近的组件中的值并将其传给theme,从而去改变CSS的样式。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36import { createContext, useContext } from 'react';
const ThemeContext = createContext(null);
export default function MyApp() {
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value="dark">
<Form />
</ThemeContext.Provider>
)
}
function Form() {
return (
<Panel title="Welcome">
<Button>Sign up</Button>
<Button>Log in</Button>
</Panel>
);
}
function Panel({ title, children }) {
const theme = useContext(ThemeContext);
const className = 'panel-' + theme;
return (
<section className={className}>
<h1>{title}</h1>
{children}
</section>
)
}
function Button({ children }) {
const theme = useContext(ThemeContext);
const className = 'button-' + theme;
return (
<button className={className}>
{children}
</button>
);
} - 在1的基础上,要做到更新主题,就可以将原来的
<ThemeContext.Provider value={theme}>中的value的值改为{theme},使用useState去更新它的值。即在父组件中声明一个状态变量,并将当前状态作为上下文值传递给Provider。如此就可以通过调用1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13function MyPage() {
const [theme, setTheme] = useState('dark');
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={theme}>
<Form />
<Button onClick={() => {
setTheme('light');
}}>
Switch to light theme
</Button>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
}setTheme来更新传递给Provider的主题值,所有Button组件都将使用新的“light”值重新渲染。
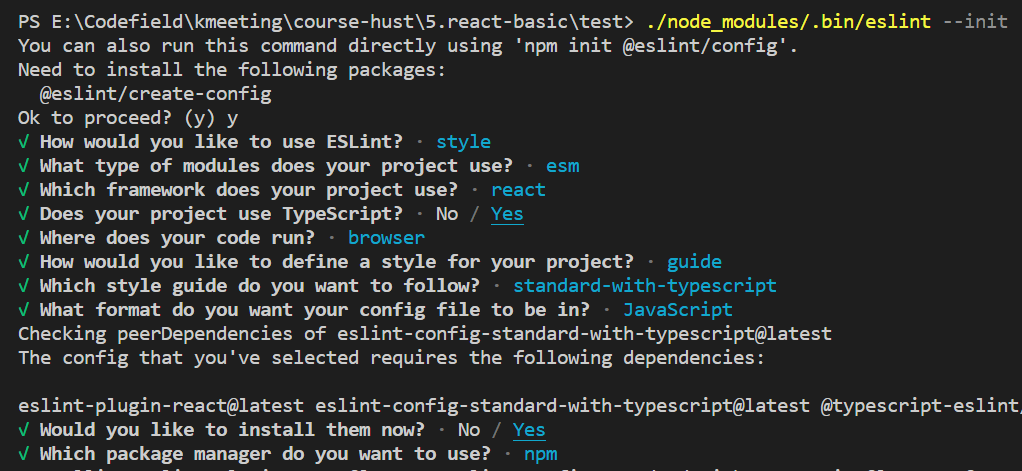
创建React项目+Eslint+Prettier
通过以下命令创建和初始化一个webpack(还缺一个React)
1
npx webpack init
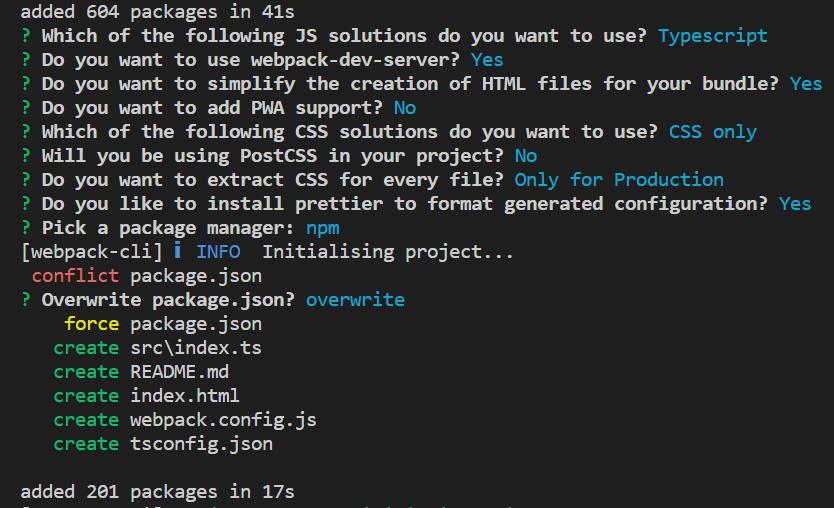
安装react相关模块
1
2
3
4
5npm i react react-dom --save
npm i @types/react @types/react-dom --save-dev
npm i eslint -D
./node_modules/.bin/eslint --init
npm i eslint-config-prettier -D